Expert Insights From Trusted Tax Advisors
Call 804-675-4593We’re Here to Teach You All About Taxes
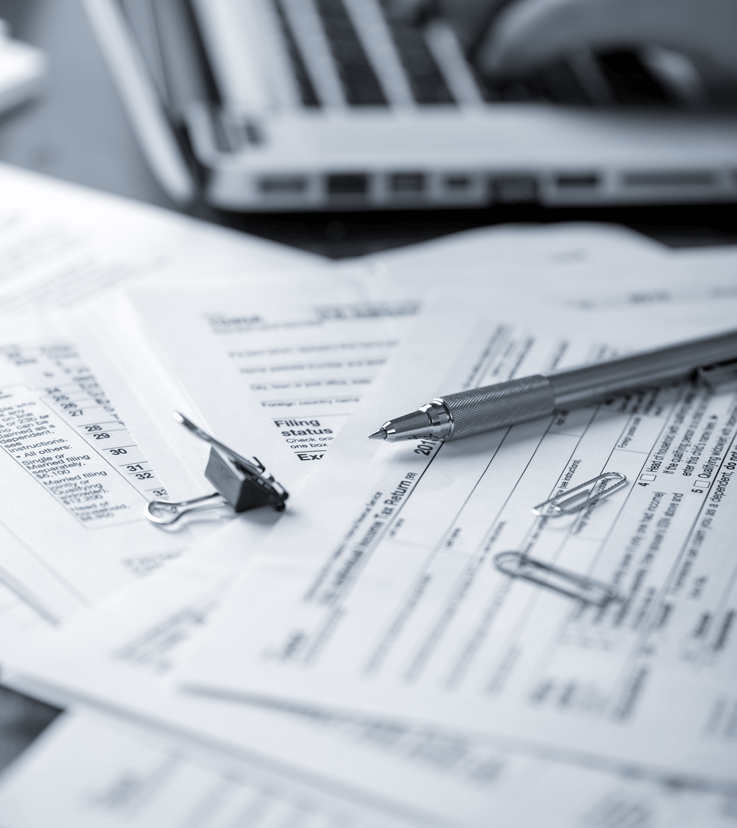
Adams Enterprises is here to be your trusted partner for expert tax preparation services in North Chesterfield, VA, and beyond. With over 41 years of experience, our tax advisors serve everyone from individuals to small businesses nationwide, specializing in military tax returns and home-based businesses. Our commitment to accuracy, prompt communication, and competitive pricing guarantees that you receive the best service possible.
We care about our clients, which is why we offer benefits such as free quotes, free phone calls, and quick turnaround times. Additionally, every completed tax return comes with a full client copy, three years of audit defense from tax protection plus, a year of identity theft restoration services up to one million dollars, and $2,500.00 in the case of a preparer error.
Our Blog
Our blog is here to be a resource for clients across the country to learn information and tips about taxes, filing, refunds, and more. Feel free to browse our range of articles that can help you navigate this tax season with ease!
Tax Tips From Josh
Cash Basis vs. Accrual Basis: Understanding the Key Differences
Cash Basis vs. Accrual Basis: Understanding the Key Differences When it comes to accounting, businesses have two primary methods for recording income and expenses: the cash basis and the accrual basis. Both approaches aim to reflect a company’s financial performance, but they do so in very different ways. Choosing between them can significantly impact how economic results are reported and interpreted. Cash Basis Accounting Cash basis accounting records revenues and expenses only when cash is exchanged. Revenue Recognition: Income is recorded when payment is received from customers. Expense Recognition: Expenses are recorded when payment is made. For example, if a company delivers a service in June but doesn’t receive payment until July, under the cash basis, the revenue would not appear on the books until July. Advantages of Cash Basis Simple to understand and implement. Provides a clear picture of cash flow at any given moment. Often suitable for small businesses and sole proprietors. Limitations of Cash Basis Does not display money owed to the business (accounts receivable). Can misrepresent financial performance by delaying recognition of revenues and expenses. Not compliant with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) for larger businesses. Accrual Basis Accounting Accrual basis accounting records revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. Revenue Recognition: Income is recorded when goods or services are delivered, regardless of when payment is received. Expense Recognition: Expenses are recorded when incurred, even if payment will be made in the future. Using the same example: if a company delivers a service in June but receives payment in July, under the accrual basis, the revenue is recorded in June—the month the service was provided. Advantages of Accrual Basis Provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance and position. Matches revenues with the expenses incurred to generate them, providing a more accurate measure of profitability. Required by GAAP and IFRS for most larger businesses. Limitations of Accrual Basis More complex to implement and maintain. May not reflect actual cash flow, since profits could be reported without having received cash. Which Method Should You Choose? The Cash Basis is generally best suited for small businesses, freelancers, and startups that prioritize simplicity and primarily deal in immediate cash transactions. The Accrual Basis is preferred (and often required) for larger businesses, companies seeking external financing, or organizations that want a complete and accurate view of their financial performance. Conclusion The cash basis and accrual basis are two distinct approaches to recording financial transactions. While the cash basis focuses on actual cash movement and offers simplicity, the accrual basis provides a more comprehensive and accurate reflection of a business’s financial health. Ultimately, the choice depends on the size, complexity, and financial reporting needs of the business. Here’s a side-by-side comparison table that highlights the main differences between Cash Basis and Accrual Basis accounting: Aspect Cash Basis Accounting Accrual Basis Accounting Timing of Revenue Recorded when cash is received. Recorded when earned, regardless of when cash is received. Timing of Expenses Recorded when cash is paid. Recorded when incurred, even if payment is later. Complexity Simple to maintain and understand. More complex, it requires tracking receivables and payables. Cash Flow Visibility Provides a clear snapshot of available cash. May not reflect actual cash on hand. Accuracy of Profit It can distort profitability if revenues/expenses are delayed. Provides a more accurate picture of profitability. Compliance Not GAAP/IFRS compliant for larger businesses. Required under GAAP/IFRS for most companies. Best Suited For Small businesses, sole proprietors, and cash-based trades. Larger businesses, companies with credit sales, and investors.
Passive Income vs. Nonpassive Income: Key Differences Explained
Passive Income vs. Nonpassive Income: Key Differences Explained Income is the foundation of financial security, but not all income is created equal. Broadly speaking, earnings can be categorized as passive income or nonpassive (active) income. Understanding the differences is crucial for financial planning, tax implications, and long-term wealth building. What Is Passive Income? Passive income refers to earnings generated with minimal ongoing effort. While it typically requires an upfront investment of time, money, or resources, the income continues to flow with minimal day-to-day involvement. Examples of Passive Income: Rental property income (after management is in place) Dividends from stocks or mutual funds Royalties from books, music, or intellectual property Affiliate marketing or automated online businesses Key Traits: Requires upfront investment or systems Generates recurring revenue Limited daily involvement once established What Is Nonpassive (Active) Income? Nonpassive income, also known as passive income, is money earned in direct exchange for time, effort, or services. In most cases, if you stop working, the income stops. Examples of Nonpassive Income: Salary or hourly wages Freelance or consulting fees Business income that requires hands-on involvement Commissions (real estate agents, sales reps, etc.) Key Traits: Tied to active participation Stops when the work stops Typically provides steady and predictable earnings Comparison Table: Passive vs. Nonpassive Income Feature Passive Income Nonpassive (Active) Income Effort Level Minimal after setup Requires ongoing work and time Examples Rentals, dividends, royalties, online sales Wages, freelance work, business ops Time Commitment Low ongoing time High – directly linked to hours worked Scalability Highly scalable with systems or investments Limited by personal capacity Stability May fluctuate with markets or demand Usually stable (salary/contract) Tax Treatment Often taxed differently under IRS rules Taxed as regular earned income Why the Distinction Matters Financial Freedom: Passive income can lead to long-term financial independence, while non-passive income provides short-term stability. Diversification: Combining both types creates a balanced income stream. Taxes: The IRS classifies and taxes these incomes differently, especially regarding losses, deductions, and self-employment tax. Wealth Building: Passive income often compounds wealth over time, whereas nonpassive income funds immediate living expenses. Final Thoughts Neither passive nor nonpassive income is inherently “better.” Non-passive income is reliable and often necessary for day-to-day living, while passive income can provide freedom and long-term growth opportunities. The key is striking the right balance—leveraging active income to cover current needs while investing in passive income streams to secure future financial independence.
I am always taking Tax Law training to stay sharp. I've been focusing on 2024 changes. This one is a whopper! WHO MUST FILE A SCHEDULE C? Schedule C is filed by those considered "Self-Employed" by the IRS. Many people are using TikTok and are getting royalties from their videos. BEWARE! If you receive the following, you must file a Schedule C on your Tax Return. 1099 MISC: This is for $600 or more in rent, $10 or more in royalties, etc. 1099 NEC - This is for $600 or more in non-employee compensation. For example, you are hired to help a landscape company and receive over $600. You are a soloist or play in a band and receive over $600 from a Funeral Home, Wedding Venue, etc. 1099K - this one bit a lot of people in 2020. It came out in 2012 but wasn't enforced until the tax year 2020. You will get this if you have $600 or more in third-party network transactions (2023). I.e., PayPal, CashApp, Venmo, etc. If you are using these Apps, it's possible that you could receive a 1099K even if you are only giving money to friends, family, charities, etc. Have your receipts or Bank Statements handy! If you receive an incorrect 1099K, a properly trained Tax Professional can get it exempted from your taxable income. W-2: Statutory Employees—If workers are independent contractors under the common law rules, they may nevertheless be treated as employees by statute (statutory employees) for certain employment tax purposes if they fall within any one of the following four categories and meet the three conditions described under Social Security and Medicare taxes, below. A driver who distributes beverages (other than milk), meat, vegetables, fruit, or bakery products or picks up and delivers laundry or dry cleaning if the driver is your agent or is paid on commission. A full-time life insurance sales agent whose principal business activity is selling life insurance, annuity contracts, or both, primarily for one life insurance company. An individual who works at home on materials or goods that you supply and that must be returned to you or to a person you name if you also furnish specifications for the work to be done. A full-time traveling or city salesperson who works on your behalf and turns in orders to you from wholesalers, retailers, contractors, or operators of hotels, restaurants, or other similar establishments. The goods sold must be merchandise for resale or supplies for use in the buyer’s business operation. The work performed for you must be the salesperson's principal business activity. If you have any questions, give us a call!
Extensions Give You More Time to File — Not to Pay
Extensions Give You More Time to File—Not to Pay Federal income taxes are due on April 15th, and Virginia state income taxes are due on May 1st. Many taxpayers are surprised to receive additional bills after filing their tax returns, even when they believe they’ve paid everything they owed at the time of filing. This happens because they didn’t pay at least 90% of their total tax liability when they filed for an extension. While extensions grant extra time to file your tax return, they do not extend the time to pay your taxes. Understanding Penalties and InterestAdams Enterprises can help calculate penalties and interest for your federal taxes. However, for Virginia state taxes, it’s more complicated. Virginia assesses penalties and interest using a daily rate that changes frequently, making it challenging to predict the exact amount owed. What Are Your Options?If you expect to owe taxes, here are two key options: Pay the full amount by the due date to avoid penalties and interest. File an extension and pay at least 90% of your estimated tax liability. To minimize stress and potential penalties, Adams Enterprises advises filing as early as possible in the tax year. Filing early gives you more time—until April 15th for federal taxes and May 1st for Virginia taxes—to gather the funds you need to pay. We’re Here to Help!Navigating tax season can be overwhelming, but Adams Enterprises is here to make it easier. Give us a call, and let us handle your taxes so you can sit back, relax, and watch your refund rise!
Can both parents claim the same child on their taxes?
"Navigating Tax Filing After Divorce: Who Gets to Claim the Kids?" In 2024, 41% of first marriages ended in divorce, leading to complex issues when children are involved—especially during tax season. A common question is: who gets to claim the children on their taxes? If there’s only one child, only one parent can claim them as a dependent. This parent can also qualify for the Head of Household (HoH) filing status, which provides beneficial tax rates and a higher standard deduction. But what about the other parent? Are they left without options if the child doesn’t live with them? Believe it or not, they can still file as Head of Household in certain cases! While the parent claiming the child for the Child Tax Credit typically qualifies for HoH status, the other parent may also qualify if they meet specific conditions. This rule helps address the situation of parents who share custody throughout the year. Adams Enterprises can guide you through these requirements to ensure you qualify for Head of Household status if eligible. Call us, and let us help you make the most of your tax filing!
Tax Credits do not always result in a refund!
Salesperson: Congratulations on your Solar Installation. You will be receiving a $12000 federal tax refund! Taxpayers often hear this from many salespersons. Unfortunately, this information is incorrect. What this taxpayer would actually receive is a $12000 federal energy tax credit. Credits reduce your taxes. If your taxable income is zero, then you will not get any of the credit that year. You don’t lose it. It carries over to the next tax year and so on until the credit is used up. However, the finance companies that these solar installers use are expecting that $12000 payment when you file your taxes. If you fail to make the payment, they will re-amortize your loan often resulting in a much higher monthly payment and a higher APR. Residential Energy Tax Credits are Non-refundable meaning that they can only reduce your tax to zero whereas a refundable tax credit results in a tax refund even if the amount owed is below zero. An example of this is the additional child tax credit or the earned income tax credit. Below is a link for all the new updated tax credits for tax year 2023. https://www.energystar.gov/about/federal_tax_credits/non_business_energy_property_tax_credits Adams Enterprises will answer any questions you may have concerning tax credits. Give us a call and let us help you!
IRS Letters
There are 5 General Types of IRS Notices and letters: Collections Audits Return Errors Return Requests General Letters The IRS sends notices and letters for the following reasons: You have a balance due. You are due a larger or smaller refund. We have a question about your tax return. We need to verify your identity. We need additional information. We changed your return. We need to notify you of delays in processing your return. Some IRS notices are sent via certified mail, such as the Notice of Intent to Levy, while others are mailed via regular post, like changes made to your tax return. Read all IRS letters and notices you receive, both certified and via regular mail. CP = Computer Paragraph - (CP) numbers (3-digit number for BMF AND IRAF, 2-digit number for IMF) are located in the upper right corner of the notices and letters. CSP = Classification Settlement Program - allows taxpayers and tax examiners to resolve worker classification cases as early in the administrative process as possible, reducing taxpayer burden. 5071C – Suspected Identity Theft. It requires you to verify your identity. CP11 – The IRS has corrected one or more mistakes on your Tax Return, often resulting in a higher tax balance. CP12 – The IRS has corrected one or more mistakes on your Tax Return, often resulting in a higher refund amount. CP27 – The IRS is notifying you that you may be eligible for the Earned Income Credit (EIC) but you didn’t claim it on your Tax Return. CP14 – You haven’t paid your taxes and the IRS is notifying you of the outstanding debt. This is always followed by a CP501 notice reminding you that you have unpaid taxes due. You will receive CP503 as your last reminder before the IRS starts getting serious. CP21A – This is a response to an amended tax return you filed. CP90 – This is a written notification, required by law, to inform you that the IRS intends to place a levy on federal payments due to you 30 days after the date of the letter. CP05 – A notice that your refund is being held while the IRS verifies the accuracy of the tax credits, income tax withholding, or business expenses have been verified. CP515 – The IRS did not receive a tax return from you by the due date. Adams Enterprises will assist you if you receive an IRS notice, even if you are not a client!
How to legally lower your tax liability
You’ve lived a good life. You’ve set aside money in retirement accounts. Then you receive a letter from your finance company stating that you are now required to start taking Required Monthly Distributions (RMDs) from all of your retirement accounts. You do the math and quickly realize that this amount of money could cause you to have to pay income taxes. You contact your Tax Professional and they tell you how the money will affect your tax situation. There is a legal way that you can reduce your taxes and help your favorite charities at the same time. Example: A Married Couple over age 72 drawing only Social Security who always takes the standard deduction. Your financial advisor tells you that your RMD is $3500 per month or $42000 per year. Your total social security earnings for the year are $32185. What does this RMD do to your tax situation? Without the RMD, your taxable income is $0 meaning you pay no taxes and you get no refund. The first way is you receive the funds and you give $41000 to your church or a favorite charity. The result is your retirement income is $42000 which causes your Social Security to be taxed at $17979. That makes your Adjusted Gross Income $59979. You gave $41000 to your church and you were able to itemize your deductions with a deduction of $41550 making your Taxable Income $18429. The Tax on this amount is $1843. In this scenario, you would be paying the IRS $1843. Your Virginia Taxes would be $0. Ouch! $1843 tax on the money you didn’t need but were forced to take! What could you have done to avoid these taxes? There is a legal way to reduce the taxable amount of these RMDs by making a Qualified Charitable Distribution (QCD). You still have to take the $42000 only this time you instruct your financial advisor to send $41000 of the $42000 to your Church. By making a QCD, your retirement income is only $1000 which eliminates the taxes on your social security. You get the Standard deduction of $28400 because you no longer need to itemize. Your Taxable income is now $0. You pay $0 in taxes and you did the exact thing with the RMD money! This difference is how that money was given to the church. In the first scenario, you get the money; you write the check to the church and take the deduction. However, the entire $42000 is taxable income. By taking the QCD route, your financial advisor sends the check directly to the church on your behalf. The church sends you the statement at the end of the year and you get the deduction (if needed). Adams Enterprises will advise you on how to legally reduce your taxes. A QCD is just one method. Ask questions! As you can see, it can keep you from having to pay taxes.


Get In Touch with Adams Enterprises
If you’re looking for an experienced tax firm that offers personalized services and prompt communication, choose Adams Enterprises! Located in North Chesterfield, VA, we serve individuals and small businesses throughout Chesterfield County and beyond. Our dedication to excellence and customer satisfaction sets us apart, and we’re committed to meeting all your tax preparation requirements at an unbeatable value. Call us today at 804-675-4593 and let our experts simplify your taxes!
Contact Us